A Firm's Long-run Average Cost Curve Is
This curve is obtained by drawing a line which touches the series of possible short-run cost curves. The long run average cost curve A.
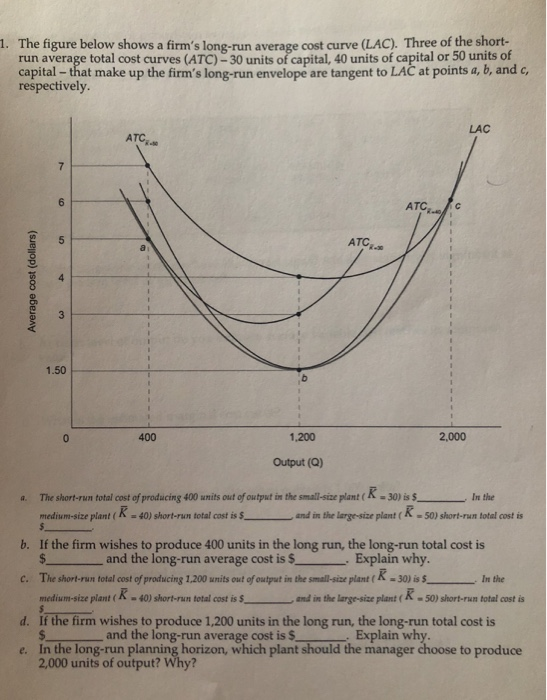
Solved I The Figure Below Shows A Firm S Long Run Average Chegg Com
The long-run average cost LRAC curve shows all possible outputs in the long run.

. Initially rises when output increases and then falls when output increases. Long Run Average Cost Long-run average cost LRAC refers to per unit cost incurred by a firm in the production of a desired level of output when all the inputs are variable. This is because a firm plans to produce an output in the long run by choosing a plant on the long run average cost curve corresponding to the output.
Opportunity cost curve c. 4 A firms long-run average cost curve is A the locus. Now what is the proper explanation of such behaviour of the long- run average cost curve.
Diminishing marginal returns C. Long run average cost is the cost per unit of output feasible when all factors of production are variable Internal economies of scale - revision video In the long run all costs are assumed to be variable. A long run average cost curve is known as a planning curve.
Mathematically speaking LRAC is the envelope of U 1 U 2 U 3 etc. What gives the long run average total cost curve its U shape are the concepts of economies of scale constant returns to scale and diseconomies of scale. A constant return to scale.
Long run average cost is long-run total cost divided by the level of output. Economies of Scale Long Run Average Costs LRAC The LRAC is simply a collection of SRAC curves. Increasing returns to scale O E diminishing marginal returns.
CM is the minimum cost at which optimum output OM can be obtained. Diseconomies of scale since average total cost is. As shown in the figure 43a the short run average cost curves which are also known as plant curves.
While the traditional shape of the Long-run cost curve is U shape the modern curve is more favourable to the L shape because technology allows for better optimization of new and old. Both relatively small and relatively large firms can be viable in the industry. The long-run average cost curve is the relationship between the lowest attainable average total cost and output when plant size is _____ and labor is _____.
Now in the long run we allow all factors of production to change so their is no more diminishing marginal product. On the left at the point where the LRAC curve has zero slope the firm is experiencing constant returns to scale. The long-run average cost LRAC curve shows the firms lowest cost per unit at each level of output assuming that all factors of production are variable.
4 A firms long-run average cost curve is. Long-run average cost curve of a firm depicts the minimum average cost at which the firm can produce any given level of output in the long run. Which of the following explains most accurately why the firms short-run.
If a firms long-run average cost curve is rising it is experiencing. Diseconomies of scale since total cost is rising as output rises. It is generally believed by economists that the long-run average cost curve is normally U shaped that is the long-run average cost curve first declines as output is increased and then beyond a certain point it rises.
In this figure 137 the long-run average cost curve of the firm is lowest at point C. Always rises as output increases. Decreasing returns to scale B.
Economies of scale are the unit cost advantages from expanding the scale of production in the long run. Long run average cost curve is also called envelope curve because it envelopes all short run average cost curves Fig. A firms long-run average cost curve decreases over a range of output because of Select the best answer below.
Firms can produce at a lower cost when output increases ie. If an industrys long-run average total cost curve has an extended range of constant returns to scale this implies that. Always falls as output increases.
Does Firm A exhibit economies or diseconomies of scale. Is the sum of a firms short run average cost curves. Technology precludes both economies and diseconomies of scale.
The LRAC curve assumes that the firm has chosen the optimal factor mix as described in the. The industry will be a natural monopoly. In the long run for Firm A total cost is 105 when output is 3 units and 120 when output is 4 units.
A firms long-run average cost curve is the boundary between attainable and unattainable cost levels with known production technologies and given factor prices In defining a firms long-run average cost curve factor prices are held constant and the quantity of. A the locus of points representing the minimum unit cost of producing any given rate of output when all inputs may be adjusted. Long run average cost curve depicts the least cost possible average cost for producing various levels of output.
What relationships do a firms short-run cost curves show. A firms long-run average cost curve is also called its _____. The long-run cost curve is a curve which shows how costs change when the scale of production is changed.
Opportunity cost curve c. B the locus of points made up of the minimum point on each short-run average total cost curve when only. No there cannot be any fixed cost in the long run.
It helps the firm decide the size of the plant for producing the desired output at the least possible cost. The long-run average cost curve is used in most meetings where all operations of a firm are being considered and are in the process of being optimized for low cost and high returns. Indicate whether each of the following statements is true or false.
Mathematically expressed the long-run average cost curve is the envelope of the SAC curves. 75 LRAC is such a line. Shows the lowest average cost facing a firm as it increases output changing both its plant and labor force.
The long run average cost LRAC is derived from short run cost curves. In the long run a firm has enough time to modify factor ratio and can change the scale of. Previous Average Cost Next Marginal Cost in Economics.
A firms long-run average cost curve is also called its _____. In the long run all inputs are variable. An increase in fixed inputs factors of production once capacity is full will shift SRAC to the right.
The point of efficient scale is the point on the long-run average cost LRAC curve where average cost for a firm is at the minimum.

Long Run Average Cost Curve Derivation Example Solved Questions Etc

Long Run Average Cost Curve Derivation Example Solved Questions Etc

Reading Short Run And Long Run Average Total Costs Microeconomics
No comments for "A Firm's Long-run Average Cost Curve Is"
Post a Comment